
Clinical features were not associated with antibody cross reactivity with any of the gangliosides or asialo-GM1, except for GD1b. In 10 (37%) of the 27 patients, anti-GM1 IgG antibody was not absorbed by any of the gangliosides or by asialo-GM1. The antibody was not absorbed by GM2, GT1b, or GQ1b. The aims of this study were to clarify the range of cross reactivity of anti-GM1 IgG antibody and to examine its relation with clinical features.Īnti-GM1 IgG antibody was absorbed effectively (20% or more absorption rate) by asialo-GM1 in 14 (52%) of 27 patients, GM1b in 11 (41%), GD1b in six (22%), and GalNAc-GD1a in five (19%, fig 1). We assume that the anti-GM1 IgG antibody has different fine specificities, which contribute to the various clinical manifestations seen in patients with GBS with anti-GM1 IgG antibody. Susuki et al 6 have shown that fine specificity of anti-GQ1b IgG antibody is closely related to the clinical manifestations deep sense disturbance is significantly present when anti-GQ1b antibody cross reacts with GD1b. Further investigation, however, is needed to determine the antibody cross reactivity, and the range of cross reactivity of the anti-GM1 IgG antibody has yet to be clarified. These antibodies seem to recognise a sugar sequence (Gal β 1–3 GalNAc β 1–4 Gal) that is common to GM1, asialo-GM1, and GD1b. Anti-asialo-GM1 and anti-GD1b antibodies in particular, are often found in patients with anti-GM1 IgG antibody. The coexistence of serum anti-GM1 antibody and antibodies to other gangliosides and asialo-GM1 occurs in some patients with GBS (reviewed by Hartung et al 5), indicative that the cross reactivity of these antibodies is due to structural homology. Antecedent upper respiratory tract infection, cranial nerve deficits, and sensory loss have been found respectively in 25%, 31%, and 19% of patients with this antibody. 2 4Patients with anti-GM1 IgG antibody, however, do not always have these features. 1-3 In addition, anti-GM1 antibody is closely associated with prior infection by Campylobacter jejuni. Patients with anti-GM1 antibody often have a motor axonal neuropathy, but they rarely show sensory disturbance and cranial nerve involvement.
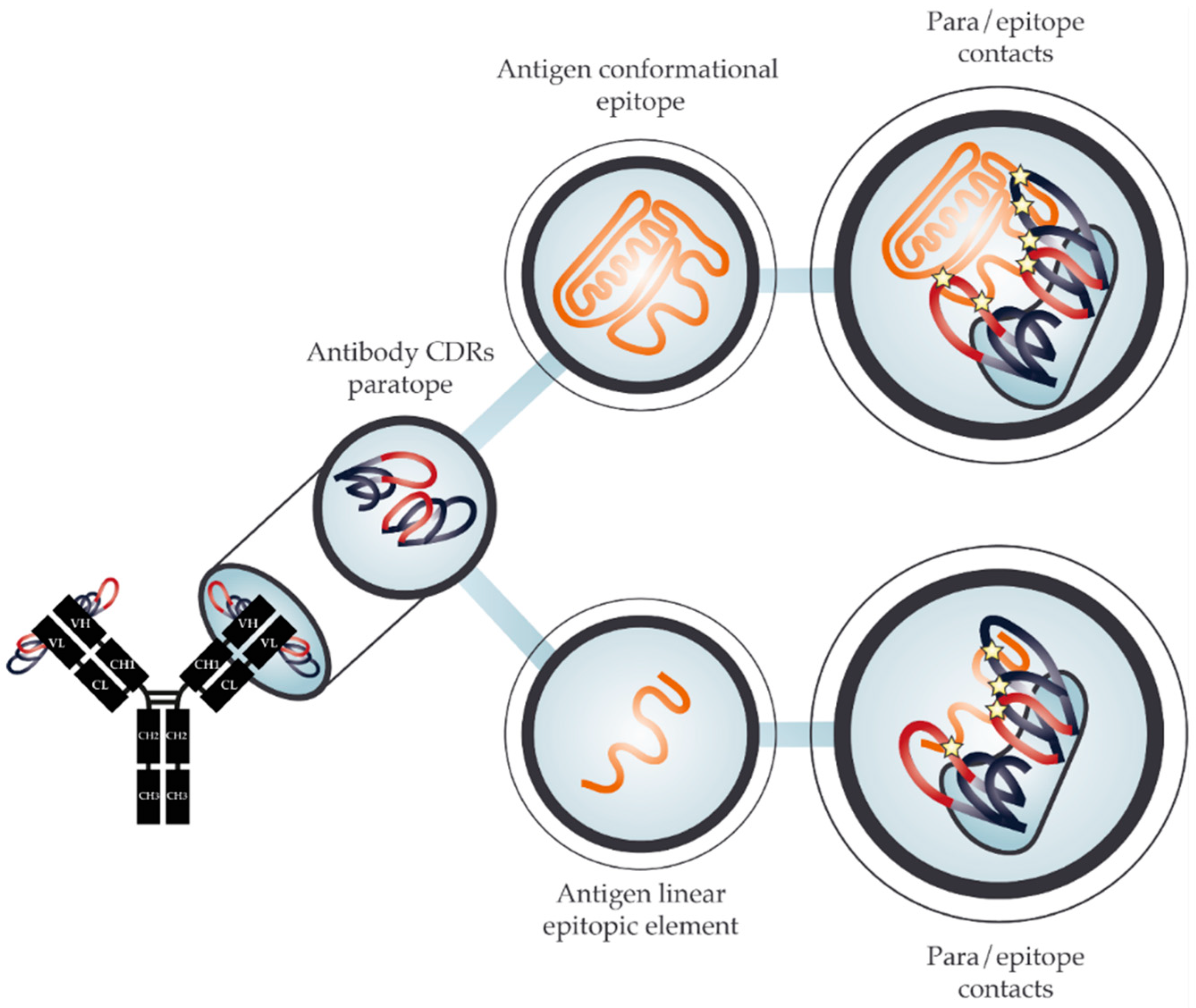
Evidence indicates that the presence of antiganglioside antibody is closely related to the clinical and electrophysiological features of GBS. The assay is adaptable to the analysis of other polymorphic antigens, rendering it a powerful tool in studies of immunity to malaria and many other diseases.Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune mediated neuropathy that has various neurological presentations. Using VAR2CSA-type PfEMP1 – a notoriously polymorphic antigen involved in the pathogenesis of placental malaria – as a model, we demonstrate the robustness of the assay and its applicability to analysis of true cross-reactivity of monoclonal VAR2CSA-specific antibodies in naturally exposed individuals. In this study, we present a further enhancement of this assay that makes direct analysis of monoclonal antibody-level cross-reactivity with allelic variants feasible. ELISpot is an assay that enables that, and a recently developed multiplexed variant of ELISpot (FluoroSpot) facilitates simultaneous assessment of B-cell/antibody reactivity to several different antigens. However, serological analysis often does not allow the distinction between true cross-reactivity (one antibody recognizing multiple antigen variants) and apparent cross-reactivity (presence of multiple variant-specific antibodies), as it requires analysis at the single B-cell/monoclonal antibody level.
The issue of antibody cross-reactivity is of central importance in immunology, and not least in protective immunity to Plasmodium falciparum malaria, where key antigens show substantial allelic variation (polymorphism).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
